Con los
diamantes,
transparencia
En Diamantes.com, te explicamos con total claridad que factores se deben tener en cuenta en el momento de elegir esta piedra preciosa, sus características esenciales y las valoraciones fundamentales que hay que tener presentes para una elección acertada y beneficiosa.
— Diamantes.com —
Bienvenido a Diamantes.com, un espacio único para descubrir y comprender la calidad de los diamantes en toda su extensión. Nuestro compromiso es guiarte a través del fascinante universo de las gemas preciosas, revelando no solo su belleza infinita, de la que seguro eres consciente, sobre todo cómo aplicar los criterios esenciales que determinan su valor y distinción entre otras piedras preciosas.
— Las 4Cs del Diamante —
La Calidad de un diamante depende de cuatro claves
La calidad de un diamante se mide a través de cuatro características fundamentales conocidas como las 4Cs: Corte, Color, Claridad y Quilate.
En Diamantes.com, desglosamos estos elementos para que puedas tomar decisiones contrastadas, ya sea en la búsqueda de una pieza de joyería única o desees invertir en diamantes.
El mercado de los Diamantes
En Diamantes.com insistimos en que el mercado de diamantes es dinámico, y los precios pueden fluctuar debido a factores económicos globales, la demanda en mercados específicos y la rareza de ciertas características. Además, la procedencia y la sostenibilidad pueden jugar un papel cada vez más importante en la valoración de los diamantes, con un número creciente de consumidores buscando opciones éticamente obtenidas.
Para obtener una estimación precisa y actualizada del precio de un diamante específico, Diamantes.com recomienda consultar con expertos y utilizar herramientas de valoración en línea, teniendo en cuenta que la mejor inversión es aquella que equilibra calidad y presupuesto, reflejando las preferencias personales del comprador.
En conjunto, las 4Cs proporcionan una forma sistemática de evaluar y comparar diamantes, ayudando a los compradores a tomar decisiones informadas y a los vendedores a determinar precios justos en el mercado.

Certificación y Cuidado de los diamantes
La autenticidad y el cuidado de tu diamante son prioritarios
Por ello, cada gema viene acompañada de una certificación de renombradas instituciones, asegurando su calidad y origen. Además, ofrecemos consejos expertos para el mantenimiento de tus diamantes, garantizando que su esplendor perdure a través de los años.
La calidad de los diamantes es un arte y una ciencia, y en Diamantes.com nos enorgullecemos de ser tus aliados en este descubrimiento. Desde la selección hasta el cuidado de tus diamantes, estamos aquí para asegurar que cada pieza que elijas, o que estudies sea eterna y de una calidad insuperable.
Información General sobre el Diamante
Categoría: Mineral
Composición química: Carbono (C)
Dureza: 10 en la escala de Mohs (máxima dureza)
Densidad: 3,5 – 3,53 g/cm³
Transparencia: Transparente a translúcido
Sistema cristalino: Isométrico (cúbico)
Índice de refracción: 2,4175 – 2,4178
El diamante es uno de los materiales naturales más destacados por sus propiedades físicas, su estructura cristalina única y su extrema dureza, lo que lo convierte en una de las gemas más preciadas y buscadas. Lo
s diamantes son alótropos de carbono formados en condiciones geológicas excepcionales que les otorgan un brillo y transparencia incomparables.

Historia de los Diamantes
Origen del Nombre del Diamante y su Significado
La palabra “diamante” proviene del griego “ἀδάμας” (adámas), que significa “irrompible” o “indomable”. Los diamantes fueron descubiertos y valorados por primera vez en la India hace más de 3000 años, donde se utilizaban como amuletos, objetos ceremoniales y símbolos de poder. A lo largo de la historia, el diamante ha simbolizado pureza y resistencia, y su uso se ha extendido en joyería y objetos de lujo.
Evolución de los Diamantes en el Mercado
Durante el siglo XIX, los diamantes adquirieron una popularidad global impulsada por el descubrimiento de minas en Sudáfrica, el crecimiento económico mundial y campañas de marketing que resaltaron el valor del diamante como símbolo de compromiso y riqueza. La compañía De Beers lideró la comercialización de los diamantes, consolidando su imagen de “eternos” y construyendo su reputación como símbolo de amor.

1. Introducción a los Diamantes
Los diamantes son una de las gemas más codiciadas y admiradas en el mundo entero. Conocidos por su brillantez, su resistencia y su valor, estas piedras preciosas han capturado la imaginación de la humanidad durante milenios. La palabra “diamante“ proviene del griego antiguo ἀδάμας (adámas), que significa “inalterable” o “irrompible“, lo que refleja su increíble dureza y durabilidad.
En la sociedad actual, los diamantes no solo representan riqueza y belleza, sino que también se han convertido en un símbolo de amor eterno, especialmente en la tradición de los anillos de compromiso. Además de su uso como gema preciosa, el diamante tiene una variedad de aplicaciones industriales gracias a sus características físicas únicas, como su extrema dureza y su capacidad para conducir el calor. En esta guía, exploraremos todo lo relacionado con los diamantes: desde su formación y características hasta su valor cultural e industrial.
2. Formación de los Diamantes
2.1. ¿Cómo se Forman los Diamantes en la Naturaleza?
Los diamantes se forman en condiciones de presión y temperatura extremas que solo se encuentran a grandes profundidades dentro de la Tierra, típicamente entre 140 y 190 kilómetros bajo la superficie, en una región conocida como el manto terrestre. El proceso de formación de un diamante natural comienza cuando el carbono presente en las profundidades de la Tierra queda expuesto a presiones de hasta 725,000 libras por pulgada cuadrada y temperaturas que varían entre 900 y 1,300 °C.

Este proceso puede durar entre 1 y 3,3 mil millones de años, lo que equivale aproximadamente entre el 75 % y el 25 % de la edad total de la Tierra. Estos diamantes se trasladan hacia la superficie de la Tierra a través de erupciones volcánicas que generan tubos de kimberlita y lamproíta, donde se encuentran incrustados.
Si quieres saber más sobre visita nuestro post – ¿Como se forman los diamantes en la naturaleza?
2.2. Formación de Diamantes por Impacto de Meteoritos
Además de formarse en el manto terrestre, los diamantes también pueden originarse a partir del impacto de meteoritos. Cuando un meteorito colisiona con la Tierra, se generan presiones y temperaturas tan extremas que permiten la formación de diamantes. Estos diamantes se conocen como diamantes de impacto y, aunque suelen ser más pequeños, su formación demuestra la increíble capacidad del carbono para transformarse bajo condiciones de alta presión.
2.3. Comparativa: Diamantes Naturales vs. Diamantes Sintéticos
Los diamantes también pueden ser creados artificialmente en laboratorios mediante técnicas que imitan las condiciones extremas del manto terrestre. Los métodos más comunes son el proceso de Alta Presión y Alta Temperatura (HPHT) y la Depósito Químico de Vapor (CVD).
Los diamantes sintéticos tienen aplicaciones tanto en joyería como en la industria, y aunque su apariencia y composición química son idénticas a las de los diamantes naturales, su valor en el mercado suele ser inferior.

Si quieres saber mas visita nuestro post del Blog – ¿Como se puede diferenciar un diamante natural de uno artificial?
3. Características Físicas y Químicas del Diamante
3.1. Estructura Cristalina del Diamante
 El diamante es un alótropo del carbono y tiene una estructura cristalina cúbica centrada en la cara, también conocida como estructura isométrica. En esta disposición, cada átomo de carbono está unido covalentemente a otros cuatro átomos de carbono en un arreglo tetraédrico, lo que le otorga al diamante su excepcional dureza. Esta disposición es la clave de muchas de las propiedades únicas del diamante, como su resistencia a los arañazos y su alta capacidad de dispersión de la luz.
El diamante es un alótropo del carbono y tiene una estructura cristalina cúbica centrada en la cara, también conocida como estructura isométrica. En esta disposición, cada átomo de carbono está unido covalentemente a otros cuatro átomos de carbono en un arreglo tetraédrico, lo que le otorga al diamante su excepcional dureza. Esta disposición es la clave de muchas de las propiedades únicas del diamante, como su resistencia a los arañazos y su alta capacidad de dispersión de la luz.
3.2. Dureza y Escala de Mohs de un Diamante
El diamante es el material natural más duro conocido, con una dureza de 10 en la escala de Mohs, que mide la resistencia de un mineral a ser rayado. Esta propiedad lo convierte en una herramienta invaluable para cortar, pulir y perforar otros materiales. Sin embargo, aunque el diamante es extremadamente duro, no es indestructible. Puede fracturarse si se golpea en una dirección específica, debido a su estructura cristalina.
¿Qué es la escal de Dureza de Mohs?
3.3. Densidad y Peso Específico
La densidad de los diamantes varía entre 3,5 y 3,53 g/cm³, dependiendo de su pureza y de la presencia de inclusiones o impurezas. La alta densidad del diamante contribuye a su peso específico, que es una propiedad importante al evaluar y tasar diamantes en la industria de la joyería.
3.4. Índice de Refracción y Propiedades Ópticas
 El índice de refracción del diamante es de aproximadamente 2,42, lo que significa que la luz se dobla significativamente al entrar en la piedra, creando un brillo intenso y un destello característico conocido como “fuego”. Esta propiedad óptica es una de las principales razones por las que los diamantes son tan apreciados en la joyería, ya que su capacidad para reflejar y refractar la luz crea un efecto visual espectacular.
El índice de refracción del diamante es de aproximadamente 2,42, lo que significa que la luz se dobla significativamente al entrar en la piedra, creando un brillo intenso y un destello característico conocido como “fuego”. Esta propiedad óptica es una de las principales razones por las que los diamantes son tan apreciados en la joyería, ya que su capacidad para reflejar y refractar la luz crea un efecto visual espectacular.
3.5. Conductividad Térmica y Propiedades Eléctricas
El diamante es un excelente conductor del calor, con una conductividad térmica de aproximadamente 2,000-2,500 W/(m·K), lo que lo hace ideal para aplicaciones industriales que requieren disipación de calor. En contraste, el diamante es un muy mal conductor eléctrico, lo que lo convierte en un excelente aislante, a excepción de algunos diamantes con impurezas de boro que actúan como semiconductores.
4. Tipos de diamantes
Diamantes según su Formación
Estos diamantes se distinguen según cómo y dónde se forman.
4.1. Diamantes Naturales
Los diamantes naturales se forman a grandes profundidades dentro del manto terrestre bajo condiciones extremas de presión y temperatura. Este proceso puede durar miles de millones de años, y los diamantes son transportados a la superficie a través de erupciones volcánicas. Cada diamante natural es único, y su valor depende de características como el corte, el color, la claridad y el peso en quilates.
4.2. Diamantes Sintéticos
Los diamantes sintéticos se producen en laboratorios mediante técnicas que imitan las condiciones del manto terrestre. Los métodos más comunes para crear diamantes sintéticos son:
- Alta Presión y Alta Temperatura (HPHT): Este método reproduce las condiciones naturales del manto terrestre y es utilizado para producir diamantes tanto para joyería como para uso industrial.
- Depósito Químico de Vapor (CVD): En este proceso, se utiliza una mezcla de gases y calor para depositar capas de carbono que forman un diamante. Los diamantes CVD son cada vez más populares en la industria de la joyería.
4.3. Diamantes de Impacto
Los diamantes de impacto se forman a partir de las condiciones de presión y temperatura generadas por el impacto de un meteorito. Aunque estos diamantes son generalmente más pequeños que los diamantes naturales, son de gran interés científico debido a su proceso de formación.
4.4. Diamantes Extraterrestres
Algunos diamantes, conocidos como diamantes carbonados o nanodiamantes, se forman en el espacio y llegan a la Tierra en meteoritos. Estos diamantes pueden haber sido creados durante explosiones de supernovas o en el medio interestelar.
4.2.0 Diamantes según su Color
El color de un diamante puede variar debido a la presencia de diferentes impurezas o a deformaciones en su estructura cristalina.
4.2.1. Diamantes Incoloros
Los diamantes incoloros son los más comunes y deseados en la industria de la joyería. Los mejores diamantes incoloros se clasifican en los grados más altos de la escala de color del GIA (de D a F), lo cual indica que no tienen ninguna tonalidad perceptible.

4.2.2. Diamantes de Colores Fantasía (Fancy Color)
Los diamantes de colores fantasía tienen tonos que van más allá del rango de color de los diamantes incoloros. Estos colores se deben a la presencia de impurezas o a defectos en la estructura cristalina:
- Diamantes Amarillos: Su color se debe a la presencia de nitrógeno. Los diamantes amarillos son relativamente comunes y son muy populares en joyería.

- Diamantes Azules: Contienen trazas de boro, que les confieren su distintivo color azul. Ejemplos famosos son el Diamante Hope y el Diamante Wittelsbach.

- Diamantes Rosados y Rojos: Los diamantes rosados y rojos son extremadamente raros y su color se atribuye a deformaciones en la estructura cristalina. El Diamante Argyle es uno de los más conocidos.
- Diamantes Verdes: Su color se debe a la exposición a la radiación natural durante su formación.

- Diamantes Marrones: Los diamantes marrones son algunos de los más comunes y su color se debe a defectos en la estructura cristalina. Son conocidos comercialmente como diamantes chocolate.
- Diamantes Negros: Contienen numerosas inclusiones de grafito que le dan un aspecto oscuro. Los diamantes negros son valorados por su aspecto único en la joyería contemporánea.

4.3.0 Diamantes según su Uso
Los diamantes también pueden clasificarse según el propósito para el que se utilizan.
4.3.1. Diamantes de Grado Gema
Los diamantes de grado gema son aquellos que tienen la claridad, el color y la calidad necesarios para ser utilizados en joyería. Estos diamantes son pulidos y cortados de manera que resalten su brillo y belleza.
4.3.2. Diamantes de Grado Industrial
Los diamantes de grado industrial no cumplen con los requisitos de calidad para ser usados en joyería debido a sus inclusiones o impurezas. Sin embargo, su dureza los hace ideales para aplicaciones industriales, como herramientas de corte, brocas y abrasivos. Aproximadamente el 80% de los diamantes extraídos se utilizan con fines industriales.
4.4.0 Diamantes según su Procedencia
Los diamantes también pueden clasificarse en función de su lugar de extracción y características relacionadas.
4.4.1. Diamantes Africanos
África es el mayor productor de diamantes naturales, con países como Botswana, Sudáfrica, Angola, y la República Democrática del Congo que destacan en la producción. Los diamantes africanos incluyen algunos de los más grandes y famosos del mundo, como el Cullinan.
4.4.2. Diamantes Canadienses
Los diamantes canadienses se extraen principalmente en los Territorios del Noroeste. Son apreciados por los consumidores que buscan diamantes éticos, ya que la minería canadiense sigue estrictos estándares ambientales y laborales.
4.4.3. Diamantes Rusos
Rusia es otro gran productor de diamantes, particularmente en la región de Yakutia. Los diamantes rusos se distinguen por su excelente calidad y claridad.
4.4.4. Diamantes Australianos
Australia es conocida principalmente por sus diamantes rosados, extraídos en la mina de Argyle, que ha sido una de las principales fuentes de diamantes de color rosa y marrón.
4.5.0 Diamantes según su Clasificación de Impurezas (Tipos I y II)
Los diamantes se pueden clasificar en diferentes tipos en función de las impurezas que contienen.
4.5.1. Tipo Ia
Los diamantes Tipo Ia contienen grupos de átomos de nitrógeno, que son responsables de darle al diamante una tonalidad amarilla. Este tipo representa aproximadamente el 95% de todos los diamantes naturales.
4.5.2. Tipo Ib
En los diamantes Tipo Ib, los átomos de nitrógeno están aislados, lo que produce un color amarillo más intenso. Los diamantes Tipo Ib son extremadamente raros y representan menos del 0.1% de los diamantes naturales.
4.5.3. Tipo IIa
Los diamantes Tipo IIa son los más puros desde el punto de vista químico, ya que contienen muy pocas impurezas o ninguna. Estos diamantes suelen ser incoloros y representan menos del 2% de los diamantes naturales. Famosos ejemplos de diamantes Tipo IIa incluyen el Cullinan y el Koh-i-Noor.
4.5.4. Tipo IIb
Los diamantes Tipo IIb contienen trazas de boro, lo que les da una conductividad eléctrica única y un color azul. Los diamantes azules más famosos del mundo, como el Diamante Hope, pertenecen a este tipo.
5. Colores de los Diamantes
5.1. Origen de los Colores en los Diamantes
Los diamantes suelen ser incoloros, pero pueden presentarse en una amplia variedad de colores debido a la presencia de impurezas o defectos estructurales. Los átomos de nitrógeno, por ejemplo, son responsables del color amarillo, mientras que el boro puede conferir un tono azul. Las deformaciones en la estructura cristalina también pueden producir colores como el rosa o el marrón.
Si quieres saber más visita nuestro post sobre – El impacto del color en el valor de los diamantes
5.2. Escala de Color de Diamantes
El color de los diamantes se clasifica según la escala del Gemological Institute of America (GIA), que va desde la letra D (incoloro) hasta la Z (amarillo o marrón claro). Los diamantes con colores más intensos y raros, como el azul, el rosa o el rojo, se consideran “diamantes fantasía” y son extremadamente valiosos debido a su rareza.
5.3. Diamantes de Color Natural y Tratados
Algunos diamantes obtienen su color de forma natural durante su proceso de formación, mientras que otros son tratados para mejorar o cambiar su color. Los tratamientos más comunes incluyen la irradiación y el recocido a altas temperaturas. Los diamantes tratados suelen tener un valor menor que los de color natural, pero ofrecen una opción atractiva para aquellos que buscan una piedra con un color distintivo a un precio más accesible.
5.4. Diamantes Famosos por su Color
Algunos de los diamantes más famosos del mundo son conocidos por su color, como el Diamante Hope, de un tono azul profundo, o el Diamante Wittelsbach, famoso por su color azul y su historia llena de misterio. Estos diamantes han sido objeto de deseo durante siglos y continúan siendo piezas icónicas en la historia de las gemas.
En este post te contamos cuales son – Los 10 diamantes más famosos de la historia
6. Propiedades Materiales y Aplicaciones del Diamante
6.1. Uso del Diamante en la Industria de la Joyería
Los diamantes son sinónimo de lujo y belleza, y su uso en la industria de la joyería es probablemente el más conocido. Se utilizan principalmente en anillos, collares, pendientes y pulseras, donde su capacidad para reflejar la luz y su durabilidad los convierten en una opción ideal para piezas que se desean conservar por generaciones. El corte, el color, la claridad y el peso en quilates son los factores principales que determinan el valor de un diamante de joyería.

6.2. Aplicaciones Industriales
Más allá de su uso ornamental, los diamantes tienen una amplia variedad de aplicaciones industriales. Su dureza extrema los convierte en la herramienta perfecta para cortar y pulir otros materiales. Los diamantes industriales se utilizan en brocas, sierras y abrasivos, y también son empleados en la perforación de pozos petroleros y en la fabricación de herramientas de precisión.
6.3. Uso del Diamante en la Ciencia y la Tecnología
En el ámbito de la tecnología, los diamantes son utilizados en aplicaciones avanzadas, como semiconductores en electrónica de alto rendimiento y como disipadores de calor para evitar el sobrecalentamiento de dispositivos electrónicos. Su conductividad térmica y su resistencia a condiciones extremas los hacen ideales para estas aplicaciones especializadas.
7. Clasificación de los Diamantes: Las 4C
7.1. Corte (Cut)
El corte es quizás el factor más importante en la belleza de un diamante, ya que determina cómo la luz interactúa con la piedra. Un buen corte maximiza el brillo, el destello y la dispersión de luz, creando el efecto conocido como “fuego”. Los cortes se clasifican como Excelente, Muy Bueno, Bueno, Regular y Pobre, dependiendo de la simetría, las proporciones y la calidad del acabado de la piedra.

7.2. Color (Color)
El color de un diamante es otro factor crucial en su valoración. La escala de colores del GIA va de D (incoloro) a Z (ligeramente amarillo o marrón). Los diamantes incoloros son los más valiosos, ya que permiten que la luz pase sin interferencias, lo cual maximiza su brillo. Los diamantes con colores más intensos y raros, como los azules y los rosados, son considerados de fantasía y son aún más valiosos.

7.3. Claridad (Clarity)
La claridad se refiere a la presencia de inclusiones internas o imperfecciones externas en un diamante. Las inclusiones son marcas naturales que se forman durante el proceso de cristalización del diamante y pueden afectar su transparencia. Los grados de claridad van desde IF (Internally Flawless, sin imperfecciones internas) hasta I3 (incluido), dependiendo de la cantidad, el tamaño y la ubicación de las inclusiones.

7.4. Quilates (Carat Weight)
El peso de un diamante se mide en quilates, donde un quilate equivale a 0,2 gramos. El tamaño de un diamante tiene un impacto significativo en su precio, pero también depende de otros factores, como la claridad, el color y el corte.
Un diamante grande con una calidad alta en todas las categorías de las 4C tendrá un valor considerablemente más alto que un diamante más pequeño o con más inclusiones.
Si quieres saber mas sobre la 4CS visita nuestra seccion – La calidad en 4CS
8. Yacimientos y Minería de Diamantes
8.1. Principales Países Productores de Diamantes
La producción de diamantes se concentra en unos pocos países, entre los cuales destacan Sudáfrica, Botswana, Rusia, Canadá, Australia y Brasil. Cada uno de estos países tiene depósitos ricos en kimberlita o lamproíta, que son las rocas ígneas que albergan diamantes. Botswana es actualmente uno de los mayores productores de diamantes de calidad gema, mientras que Rusia tiene algunos de los depósitos más grandes del mundo.
8.2. Métodos de Extracción
Existen varios métodos para extraer diamantes, incluyendo la minería a cielo abierto, la minería subterránea y la minería aluvial.
La minería a cielo abierto se utiliza cuando los depósitos de diamantes están cerca de la superficie, mientras que la minería subterránea se emplea para acceder a depósitos más profundos.
En la minería aluvial, los diamantes se extraen de sedimentos depositados en ríos y costas, donde han sido transportados desde su lugar de origen por la acción del agua.

8.3. Impacto Ambiental y Regulaciones
La minería de diamantes tiene un impacto significativo en el medio ambiente, ya que requiere la remoción de grandes cantidades de tierra y la alteración de paisajes naturales. Para mitigar estos efectos, se han implementado regulaciones estrictas en muchos países productores, y algunas empresas mineras se han comprometido a restaurar las áreas explotadas y minimizar el impacto ecológico.
Además, el Proceso Kimberley se estableció para prevenir la comercialización de diamantes de sangre y asegurar que los diamantes se extraigan de manera ética.
9. Certificación de los Diamantes
9.1. ¿Qué es un Certificado Gemológico?
Un certificado gemológico es un documento emitido por un laboratorio especializado que describe las características de un diamante, incluyendo el corte, el color, la claridad y el peso en quilates. Este certificado proporciona al comprador la seguridad de que el diamante ha sido evaluado de manera independiente y de acuerdo con estándares establecidos.
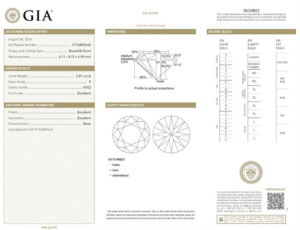
9.2. Principales Institutos de Certificación
 Los laboratorios de certificación más reconocidos a nivel mundial incluyen el Gemological Institute of America (GIA), el International Gemological Institute (IGI) y HRD Antwerp. Cada uno de estos institutos sigue procedimientos estrictos para evaluar y clasificar diamantes, y sus certificados son ampliamente respetados en el mercado internacional.
Los laboratorios de certificación más reconocidos a nivel mundial incluyen el Gemological Institute of America (GIA), el International Gemological Institute (IGI) y HRD Antwerp. Cada uno de estos institutos sigue procedimientos estrictos para evaluar y clasificar diamantes, y sus certificados son ampliamente respetados en el mercado internacional.
9.3. Cómo Leer un Certificado de Diamante
Un certificado de diamante contiene información detallada sobre las 4C, así como un diagrama de inclusiones y un número de serie único que puede estar grabado con láser en el cinturón del diamante. Al leer un certificado, es importante prestar atención a cada una de las categorías de las 4C, ya que estas determinarán la calidad y el valor de la piedra.
9.4. Precios de Certificación y Verificación en Línea
El costo de certificar un diamante puede variar dependiendo del laboratorio y del tamaño del diamante, pero generalmente oscila entre 50 y 200 euros. Los certificados también se pueden verificar en línea ingresando el número de serie en la base de datos del laboratorio emisor, lo que proporciona una capa adicional de seguridad al comprador.
Si quieres saber mas visita nuestra Guía completa sobre Certificado de diamantes
10. Diamantes Famosos en la Historia
10.1. El Cullinan: El Diamante Más Grande Jamás Encontrado
El Cullinan es el diamante más grande jamás hallado, con un peso original de 3,106 quilates. Fue descubierto en Sudáfrica en 1905 y posteriormente se dividió en varias piedras más pequeñas, algunas de las cuales forman parte de las Joyas de la Corona Británica. El Cullinan es conocido no solo por su tamaño, sino también por su claridad excepcional.

10.2. El Koh-i-Noor: Un Diamante Lleno de Misterio
El Koh-i-Noor, cuyo nombre significa “Montaña de Luz“, es uno de los diamantes más legendarios del mundo. Se cree que fue descubierto en la India hace más de 800 años y ha sido parte de las coronas de varios monarcas a lo largo de la historia. Actualmente, forma parte de las Joyas de la Corona Británica y está rodeado de leyendas sobre maldiciones y poderes mágicos.
10.3. Diamante Hope: Leyendas y Misterios
El Diamante Hope es famoso por su profundo color azul y su historia llena de misterio. Se cree que trae mala suerte a sus propietarios, una leyenda que ha sido alimentada por las tragedias sufridas por quienes lo han poseído. Hoy en día, el Diamante Hope se encuentra en exhibición en el Museo Nacional de Historia Natural del Instituto Smithsoniano en Washington D.C.
Si quieres visitar alguno de estos museo en este post te mostramos – Los mejores Museo del mundo para ver diamantes famoso
10.4. Otros Diamantes Famosos
Existen muchos otros diamantes famosos, como el Diamante Wittelsbach, conocido por su color azul, y el Diamante Orlov Negro, que tiene una historia intrigante. Estos diamantes han pasado por manos de reyes, emperadores y magnates, y cada uno tiene una historia única que lo convierte en una pieza invaluable tanto desde el punto de vista histórico como gemológico.
Los 10 diamantes más Famosos de la Historia
11. Simulantes del Diamante
11.1. ¿Qué son los Simulantes del Diamante?
Los simulantes del diamante son materiales que se parecen al diamante en apariencia, pero no comparten las mismas propiedades químicas y físicas. Estos simulantes se utilizan como alternativas más asequibles a los diamantes naturales y sintéticos. Aunque pueden parecer idénticos a simple vista, los simulantes suelen tener diferentes niveles de dureza, brillo y características ópticas que los distinguen de los diamantes verdaderos.
11.2. Comparación entre Diamantes y Simulantes
Existen varios simulantes del diamante en el mercado, siendo los más comunes la zirconia cúbica y la moissanita. La zirconia cúbica es uno de los simulantes más utilizados debido a su bajo costo y su brillo convincente. La moissanita, por otro lado, es más cara que la zirconia cúbica, pero presenta un brillo y una refracción de luz que se asemejan más al diamante.
Zirconia Cúbica: Es el simulante más conocido debido a su parecido visual con el diamante. Sin embargo, su dureza es menor (8-8.5 en la escala de Mohs) y tiene un brillo menos intenso.
Moissanita: Aunque es más cara que la zirconia cúbica, la moissanita tiene un índice de refracción más alto, lo que le otorga un destello característico que a veces la hace parecer más brillante que un diamante. Su dureza es de 9.25 en la escala de Mohs, lo que la hace más duradera que otros simulantes.
11.3. Cómo Distinguir un Diamante Real de un Simulante

Distinguir un diamante real de un simulante puede ser difícil sin el equipo adecuado, pero existen algunas pruebas que pueden ayudar:
Prueba de la Luz UV: Los diamantes reales suelen mostrar fluorescencia bajo luz ultravioleta, mientras que muchos simulantes no presentan esta característica.
Prueba de la Conductividad Térmica: Los diamantes son excelentes conductores de calor, mientras que los simulantes generalmente no lo son. Existen dispositivos portátiles que permiten medir esta propiedad para diferenciar un diamante real de uno falso.
Prueba de la Niebla: Si respiras sobre un diamante, la niebla desaparece casi instantáneamente debido a la alta conductividad térmica. En los simulantes, la niebla tarda más en disiparse.
12. La Industria del Diamante
12.1. Extracción y Comercio de Diamantes
La industria del diamante se divide principalmente en dos segmentos: la extracción de diamantes brutos y el comercio de diamantes pulidos. Los diamantes brutos se extraen en minas ubicadas en regiones como África, Canadá, Rusia y Australia, y luego son vendidos a empresas que se encargan de su corte y pulido para convertirlos en gemas aptas para la joyería.
12.2. Procesamiento y Corte de Diamantes
El corte de un diamante es un arte que requiere habilidad y precisión, ya que un mal corte puede disminuir considerablemente el valor de la piedra. Las principales ciudades donde se realiza el corte de diamantes son Amberes, Surat, Tel Aviv y Nueva York. Cada diamante es tallado para maximizar su brillo y minimizar la pérdida de peso durante el proceso de corte.
12.3. El Papel de De Beers y la Regulación del Mercado
La compañía De Beers ha desempeñado un papel clave en la regulación del mercado de diamantes durante el siglo XX. A través de la Diamond Trading Company (DTC), De Beers controló la oferta de diamantes en el mercado para mantener su valor. Aunque el mercado se ha diversificado en las últimas décadas, De Beers sigue siendo uno de los principales actores en la industria.
12.4. Tendencias Actuales en la Industria del Diamante
En la actualidad, la industria del diamante enfrenta varios desafíos y oportunidades. El auge de los diamantes sintéticos, la creciente preocupación por la sostenibilidad y la demanda de diamantes éticos están cambiando la dinámica del mercado. Cada vez más consumidores prefieren diamantes que sean extraídos de manera responsable y que no estén asociados con conflictos, lo que ha impulsado iniciativas como el Proceso Kimberley.
Si te parece interesante visita nuestro post sobre – ¿Cómo evolucionara la industri de los diamantes en los proximos 10 años?
13. Diamantes de Inversión

Los diamantes han sido considerados durante mucho tiempo una inversión segura debido a su valor intrínseco y su resistencia al paso del tiempo. A diferencia de otros activos, como los metales preciosos o el mercado de valores, los diamantes no están sujetos a las mismas fluctuaciones económicas. Además, son un bien físico que se puede almacenar y transportar fácilmente.
13.2. Diferencias entre Diamantes de Inversión y Diamantes para Joyería
No todos los diamantes son aptos para la inversión. Los diamantes de inversión suelen tener una alta calidad en términos de las 4C (Corte, Color, Claridad y Quilates) y deben estar certificados por laboratorios reconocidos como el GIA. Los diamantes de joyería, por otro lado, pueden tener características que los hacen atractivos estéticamente, pero no necesariamente cumplen con los requisitos de calidad para ser considerados una inversión sólida.
13.3. Consejos para Comprar Diamantes como Inversión
Certificación: Asegúrate de que el diamante esté certificado por un laboratorio de renombre, como el GIA o el IGI.
Calidad sobre Cantidad: Es mejor invertir en un diamante pequeño de alta calidad que en uno grande con muchas inclusiones o un color menos deseable.
Evitar Diamantes Tratados: Los diamantes tratados para mejorar su color o claridad no suelen ser una buena opción de inversión, ya que su valor es inferior al de los diamantes naturales sin tratamientos.
13.4. Evolución del Mercado de Diamantes y Previsiones a Futuro
El mercado de diamantes está en constante evolución, con un aumento en la producción de diamantes sintéticos y una mayor demanda de diamantes éticos y sostenibles. Las previsiones indican que la demanda de diamantes naturales seguirá siendo alta, especialmente para piedras de alta calidad, mientras que los diamantes sintéticos probablemente captarán una porción significativa del mercado debido a su precio accesible.
Si quieres saber más sobre como invertir en diamantes visita nuestro siguiente post.
Cómo Invertir en Diamantes: Tu primera Inversión de Diamantes
14. Diamantes y Sostenibilidad
14.1. Impacto Ambiental de la Minería de Diamantes
La minería de diamantes tiene un impacto considerable en el medio ambiente, ya que requiere la extracción de grandes cantidades de tierra y recursos naturales. Las operaciones mineras pueden alterar el paisaje, afectar los ecosistemas locales y consumir grandes cantidades de agua y energía. Para mitigar estos efectos, algunas empresas mineras han adoptado prácticas más sostenibles y han implementado planes de restauración para las áreas afectadas.
14.2. Iniciativas de Minería Ética y Sostenible
En respuesta a las preocupaciones sobre el impacto ambiental y los diamantes de conflicto, se han desarrollado iniciativas para promover la minería ética. El Proceso Kimberley es uno de los esfuerzos más importantes para evitar que los diamantes extraídos de zonas de conflicto lleguen al mercado. Además, muchas empresas están optando por trabajar con diamantes certificados como libres de conflicto, lo que garantiza que se extraen de manera responsable y sin financiar conflictos armados.
14.3. Diamantes Sintéticos: ¿Una Alternativa Más Ética?
Los diamantes sintéticos son cada vez más populares entre los consumidores que buscan una alternativa más ética y sostenible. Estos diamantes se producen en laboratorios, lo que elimina los problemas asociados con la minería, como la degradación del medio ambiente y la explotación laboral. Además, los diamantes sintéticos tienen una huella de carbono significativamente menor, lo que los convierte en una opción atractiva para los compradores preocupados por el medio ambiente.
14.4. Programas y Regulaciones Internacionales
Además del Proceso Kimberley, otras organizaciones y programas trabajan para promover prácticas sostenibles en la industria del diamante. El Responsible Jewellery Council (RJC) es una organización que establece estándares para la extracción responsable de minerales preciosos y gemas, incluyendo los diamantes. Las empresas que cumplen con estos estándares pueden obtener la certificación RJC, lo que garantiza a los consumidores que sus productos se obtienen de manera ética y sostenible.
15. El Papel de los Diamantes en la Cultura
15.1. Historia de los Diamantes como Símbolos de Poder y Riqueza
 Desde la antigüedad, los diamantes han sido símbolo de poder, riqueza y prestigio. Los antiguos griegos y romanos creían que los diamantes eran fragmentos de estrellas caídos del cielo o lágrimas de los dioses. Durante la Edad Media, los diamantes eran usados por la realeza y la nobleza para demostrar su estatus, y también se les atribuían propiedades mágicas y curativas.
Desde la antigüedad, los diamantes han sido símbolo de poder, riqueza y prestigio. Los antiguos griegos y romanos creían que los diamantes eran fragmentos de estrellas caídos del cielo o lágrimas de los dioses. Durante la Edad Media, los diamantes eran usados por la realeza y la nobleza para demostrar su estatus, y también se les atribuían propiedades mágicas y curativas.
15.2. Los Diamantes en las Tradiciones de Compromiso y Matrimonio
Los diamantes se han convertido en el símbolo definitivo del amor y el compromiso. Esta tradición comenzó en 1477, cuando el archiduque Maximiliano de Austria le entregó un anillo de compromiso con un diamante a María de Borgoña. Sin embargo, fue en el siglo XX cuando los diamantes se popularizaron como la piedra preferida para los anillos de compromiso, gracias a una campaña de marketing de De Beers que acuñó el famoso lema “Un diamante es para siempre”.
15.3. La Influencia de la Mercadotecnia en la Popularidad de los Diamantes
La campaña publicitaria de De Beers fue fundamental para establecer la idea de que un anillo de compromiso debía tener un diamante. A través de anuncios y el uso de celebridades, De Beers logró que los diamantes se convirtieran en un símbolo de amor eterno y compromiso. Esta estrategia de marketing no solo incrementó las ventas de diamantes, sino que también consolidó su lugar en la cultura popular.
15.4. Referencias a los Diamantes en el Arte, la Música y el Cine
Los diamantes han sido una fuente de inspiración en el arte, la música y el cine. Canciones como “Diamonds Are a Girl’s Best Friend” de Marilyn Monroe y “Shine Bright Like a Diamond” de Rihanna destacan la fascinación de la cultura popular por estas gemas. En el cine, películas como “Diamantes de Sangre” han abordado tanto la belleza de los diamantes como los conflictos éticos que los rodean.
16. Consejos para Comprar un Diamante
16.1. Factores a Tener en Cuenta: Las 4C
Al comprar un diamante, es esencial tener en cuenta las 4C: Corte, Color, Claridad y Quilates. Estos factores determinan la calidad y el valor del diamante. Asegúrate de entender cómo cada uno de estos aspectos afecta el precio y la apariencia de la piedra.
16.2. Cómo Evitar Estafas y Comprar Diamantes Auténticos
Para evitar estafas, siempre compra diamantes de un vendedor de confianza y solicita un certificado emitido por un laboratorio reconocido, como el GIA o el IGI. Además, asegúrate de comparar precios y características antes de tomar una decisión.
16.3. Compra en Línea vs. Compra en Tiendas Físicas
La compra de diamantes en línea se ha vuelto cada vez más popular debido a la comodidad y la posibilidad de comparar una amplia variedad de piedras. Sin embargo, es importante asegurarse de que la tienda en línea sea confiable y ofrezca una política de devolución en caso de que el diamante no cumpla con tus expectativas.
16.4. Preguntas Clave que Hacer al Vendedor
Antes de comprar un diamante, es importante hacer preguntas clave, como:
¿Está certificado el diamante?
¿Cuál es el grado de cada una de las 4C?
¿El diamante ha sido sometido a algún tratamiento?
¿Cuál es la política de devolución y garantía?
17. Mantenimiento y Cuidado de los Diamantes
17.1. Limpieza y Cuidado Diario de los Diamantes
 Para mantener el brillo de un diamante, es importante limpiarlo regularmente. Puedes limpiarlo en casa utilizando una solución suave de agua tibia y jabón y un cepillo de cerdas suaves. Evita el uso de productos químicos agresivos que puedan dañar el metal de la montura o afectar la piedra.
Para mantener el brillo de un diamante, es importante limpiarlo regularmente. Puedes limpiarlo en casa utilizando una solución suave de agua tibia y jabón y un cepillo de cerdas suaves. Evita el uso de productos químicos agresivos que puedan dañar el metal de la montura o afectar la piedra.
17.2. Cómo Almacenar los Diamantes para Evitar Daños
Cuando no estés usando tus joyas de diamantes, guárdalas en un lugar seguro, preferiblemente en un estuche de joyería con compartimentos individuales para evitar que los diamantes se rayen entre sí o dañen otras piezas de joyería.
17.3. Reparación de Joyas de Diamantes
Si una joya de diamante se daña o la montura se afloja, es importante llevarla a un joyero profesional para su reparación. Nunca intentes reparar una joya de diamantes en casa, ya que podrías dañar la piedra o el engaste.
18. Preguntas Frecuentes sobre Diamantes
18.1. ¿Cuáles son las Diferencias entre un Diamante Natural y uno Sintético?
Los diamantes naturales se forman en la naturaleza a lo largo de miles de millones de años, mientras que los diamantes sintéticos se crean en laboratorios en cuestión de semanas. Aunque tienen la misma composición química, los diamantes naturales son más valorados debido a su origen y su rareza.
18.2. ¿Cómo se Determina el Valor de un Diamante?
El valor de un diamante se determina en función de las 4C: Corte, Color, Claridad y Quilates. Además, la procedencia, la certificación y la demanda del mercado también juegan un papel importante en la valoración de un diamante.
18.3. ¿Qué Hace que Algunos Diamantes Sean Más Valiosos que Otros?
Los diamantes incoloros, con una alta claridad y un buen corte, suelen ser los más valiosos. Además, los diamantes de colores fantasía, como los rosados y azules, son extremadamente raros y, por lo tanto, tienen un valor mucho mayor que los diamantes incoloros comunes.
18.4. ¿Es Seguro Invertir en Diamantes?
Invertir en diamantes puede ser seguro si se hace con conocimiento y precaución. Es importante comprar diamantes certificados, de alta calidad, y tener en cuenta que los diamantes de inversión deben ser considerados como un activo a largo plazo.
18.5. ¿Qué son los Diamantes de Sangre y Cómo se Evitan?
Los diamantes de sangre son diamantes extraídos en zonas de conflicto y cuyas ventas financian actividades bélicas. Para evitar comprar diamantes de sangre, asegúrate de que el diamante esté certificado como libre de conflictos bajo el Proceso Kimberley, que garantiza que la piedra se ha obtenido de manera ética.
19. Conclusión
Los diamantes son mucho más que simples piedras preciosas; representan una combinación de ciencia, historia, cultura y valor. Ya sea que busques comprar un diamante como inversión, como símbolo de amor eterno, o simplemente para

