1. Introduction to our Guide to Diamond Certification
Diamond certification is a fundamental process for ensuring the authenticity and quality of these precious stones. When a buyer invests in a diamond, it is essential to know exactly what they are purchasing, and a gemological certificate provides that assurance. In this comprehensive guide, you will learn what diamond certification is, the main certification institutes, and how to understand a gemological certificate.
2. What is a Diamond Certificate?
A diamond certificate, also known as a gemological report, is a document issued by a specialized gemological laboratory that evaluates and describes the characteristics of the diamond. This certificate provides details such as carat weight, color, clarity, cut, and other attributes that determine the diamond’s value.
- Evaluated Characteristics: A diamond certificate describes several important characteristics of the diamond, commonly known as the “4Cs” of a diamond: Cut, Color, Clarity, and Carat Weight.
- Importance: Certification assures the buyer that the diamond has the characteristics described by the seller and allows comparisons with other stones based on objective attributes.
3. The 4Cs of a Diamond
3.1. Cut
The cut of a diamond refers to the quality of the stone’s design and finish. A good cut maximizes the diamond’s brilliance, while a poor cut can make the stone look dull or less shiny.
- Cut Grades: Cuts are evaluated with grades such as Excellent, Very Good, Good, Fair, and Poor.
- Importance: A diamond with an excellent cut will reflect light more effectively, directly influencing its appearance and value.
3.2. Color
The color of a diamond is graded on a scale from D (colorless) to Z (yellowish or brownish tones). The more colorless a diamond is, the higher its value.
- Color Scale: The most commonly used color scale is the one established by the GIA, ranging from D to Z.
- Importance: Colorless diamonds allow light to pass through without interference, maximizing brightness and light dispersion.

3.3. Clarity
Clarity refers to the presence of internal inclusions or external imperfections in a diamond. These imperfections can affect the stone’s appearance and value.
- Clarity Grades: Ranges from IF (Internally Flawless) to I3 (Included), depending on the number, size, and visibility of inclusions.
- Importance: Fewer inclusions mean higher clarity and a higher value for the diamond.
3.4. Carat Weight
A diamond’s weight is measured in carats, with one carat equaling 0.2 grams. The size of the diamond has a significant impact on its price.
- Importance of Weight: The higher the carat weight, the more expensive the diamond, provided the other characteristics are similar.
4. Main Diamond Certification Institutes
There are several globally recognized gemological laboratories that offer diamond certification. These laboratories are distinguished by the accuracy and reliability of their reports.
4.1. GIA (Gemological Institute of America)

The GIA is one of the most renowned and respected certification laboratories in the world. It established the “4Cs” scale and is known for its precision in diamond evaluation.
- Certificate Features: The GIA certificate includes details such as the 4Cs, a diagram of the inclusions, and the laser-inscribed serial number of the diamond.
- Importance: GIA certificates are highly valued in the industry and provide a strong guarantee of diamond quality.
4.2. IGI (International Gemological Institute)
The IGI is another well-known institute for diamond certification, especially popular for certifying diamonds in commercial jewelry.
- Differences with GIA: IGI reports tend to be more cost-effective, but some buyers consider their evaluations less strict compared to the GIA.
- Importance: IGI is a good option for those seeking reliable certification, although it may not be as rigorous as GIA’s.
4.3. HRD Antwerp
HRD Antwerp is a European certification institute that offers detailed diamond analyses and follows standards very similar to those of the GIA.
- European Approach: Particularly popular in Europe and known for its meticulous attention to detail in certification.
5. How to Read a Diamond Certificate
A diamond certificate includes a wealth of technical information that may seem complicated at first. Here is how to understand the most important elements:
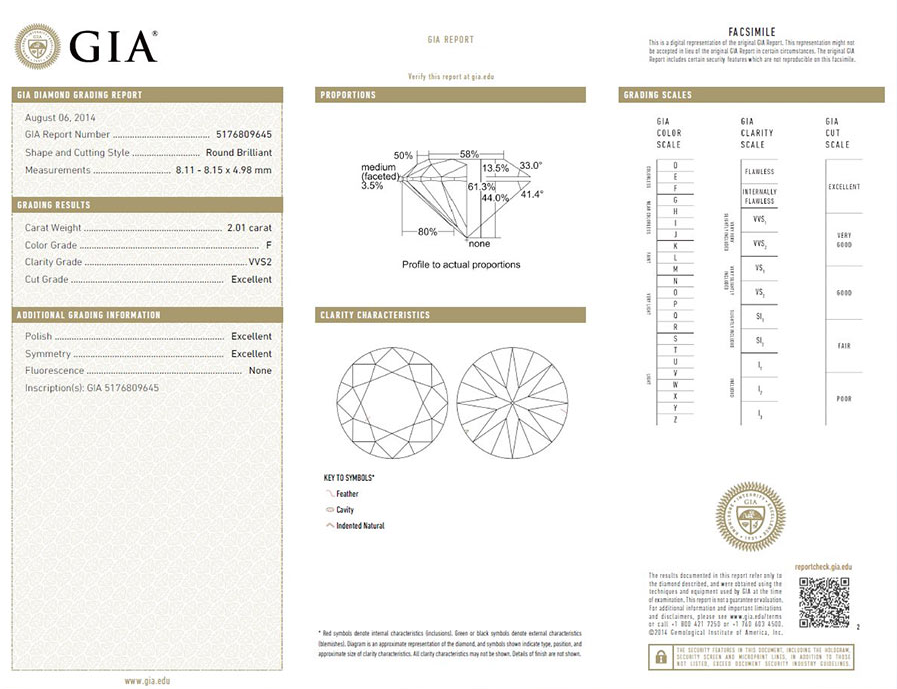
5.1. Certificate Number
Every certified diamond has a unique certificate number, which may also be laser-inscribed on the diamond’s girdle for identification purposes.
- Importance: This allows the diamond’s authenticity to be verified in the issuing laboratory’s database.
5.2. Inclusion Diagram
Many certificates, especially GIA ones, include a diagram showing the location of the diamond’s inclusions and imperfections.
- Interpretation: The marks on the diagram indicate the type and location of each inclusion, helping you understand the diamond’s clarity.
5.3. Color, Cut, and Clarity Scales
The certificate also includes scales for color, cut, and clarity, with grades for each of these characteristics.
- Understanding: These scales are essential for comparing diamonds and determining which offers the best value for money.

6. How to Verify a Diamond Certificate
6.1. Online Verification
Most certification institutes allow buyers to verify certificates online by entering the diamond’s serial number.
Example: If you have a GIA certificate, you can go to the official Gemological Institute of America (GIA) website and enter the certificate number to check its authenticity.
6.2. What to Look for in a Fake Certificate
Some dishonest sellers may provide counterfeit certificates. To avoid this, make sure to:
- Check the Logo and Print Quality: Authentic certificates will have well-printed logos and text.
- Verify with the Laboratory: Always verify the certificate directly with the issuing laboratory.
Certifying a diamond is essential for ensuring its authenticity and knowing its specific characteristics. In Spain, there are several recognized gemological laboratories that offer certification services. Below are some of them:
- Instituto Gemológico Español (IGE): Founded in 1969, the IGE is a reference in Spain for its rigor and independence. It offers analysis and certification of gems, including diamonds.
- GEMACYT Laboratorio Gemológico: Since 1992, GEMACYT has been dedicated to the certification of diamonds, precious stones, and jewelry pieces, as well as offering appraisal and training services.




